I’ve used the below process several times during failed upgrades or downsizing of a Horizon pod. I’ve become strangely well versed with this procedure after working with a customer using Horizon 2111.2 and seeing various errors during upgrades that gave us no fix-forward choice, despite Omnissa support involvement.
The process combines the Omnissa guidance and some tips from Omnissa GSS.
Before Starting: Check FSMO Schema role owner
This prerequisite ensures you don’t see replication errors between the remaining healthy pod members. This can happen if you were to accidentally uninstall a connection server that was holding the local/global schema roles. If required, seize the role owner to another connection server instance.
Check the configuration and schema role owner and seize it to another connection server
- From a connection server instance, open LDP.exe > Connection > Connect > localhost
- Connection > Bind > Select Bind as currently logged on user
- Click View > Tree > select CN=Schema, CN=configuration from the drop-down menu.
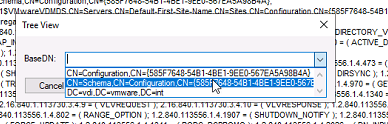
4. Search for the output for the text string “fsMORoleOwner “. The hostname of the owner will be displayed.

5. To seize the role to another connection server, first log onto the server you wish to seize the role.
Run the below command from an elevated command prompt. If the horizon pod has CPA enabled, there will be a Schema master for the local ADAM database. There will also be one for the global ADAM database. Remember to assign both roles to a different server.
cd c:\Program Files\VMware\VMware View\Server\tools\bin\
vdmadmin -x -seizeSchemaMaster
vdmadmin -x -seizeSchemaMaster -global Uninstall Connection Server
6. Disable the connection server in Horizon Administration console by logging into https://ConnectionServer.domain.com/admin > Servers > Connection Servers > select target > Disable
7. Uninstall the components from appwiz.cpl or Add/Remove Programs: Horizon Connection Server, HTML Component, VMwareVDMDS and VMwareVDMDSG.
8. Remove VDM registry keys.
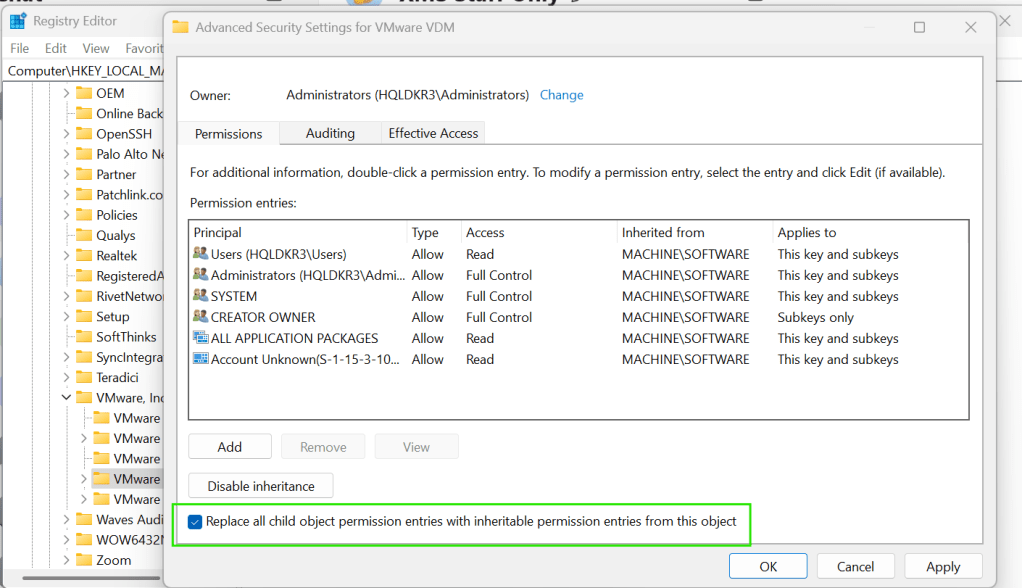
Right click HKLM\Software\VMWare…\VDM> Permissions > Advanced > select ‘Replace all child object permission entries with inheritable permission entries from this object’ > Apply > Ok.
Delete the parent key: HKLM\Software\VMWare…\VDM
9. Open the local Certificate Store > Personal > VMware View Connection Server > Delete all certificates within the store.
10. Reboot the server.
Remove references to unwanted connection server via vdmadmin
11. Use the below vdmadmin command to remove references to the unwanted connection server in the ADAM database. This command must be run from another connection server instance and is case sensitive.
cd C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware View\Server\tools\bin\
vdmadmin -S -r -s <NetBIOSName> Check replication health
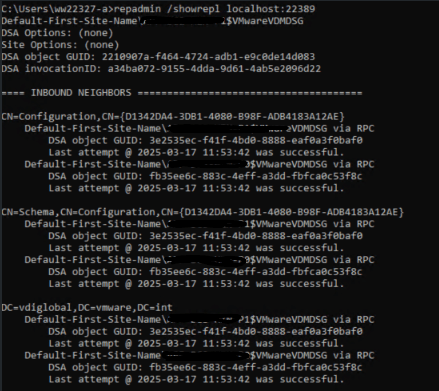
11. From any connection server instance command prompt, check replication health on the local ADAM database. The local ADAM database uses port 389. You can also check the global ADAM database, which uses port 22389.
repadmin /showrepl localhost:389
repadmin /showreplc localhost:22389The output should display replication connections between the existing local pod members, and for CPA, remote pods.
12. Login to the connection server administration console and verify the node has been removed from the list of connection servers.
Summary
After removing the connection server, the installation directory in Program Files will still contain some configuration files. This is intentional. It can be useful if you choose to rebuild the installation. It is also helpful if you need to back up the old configuration.